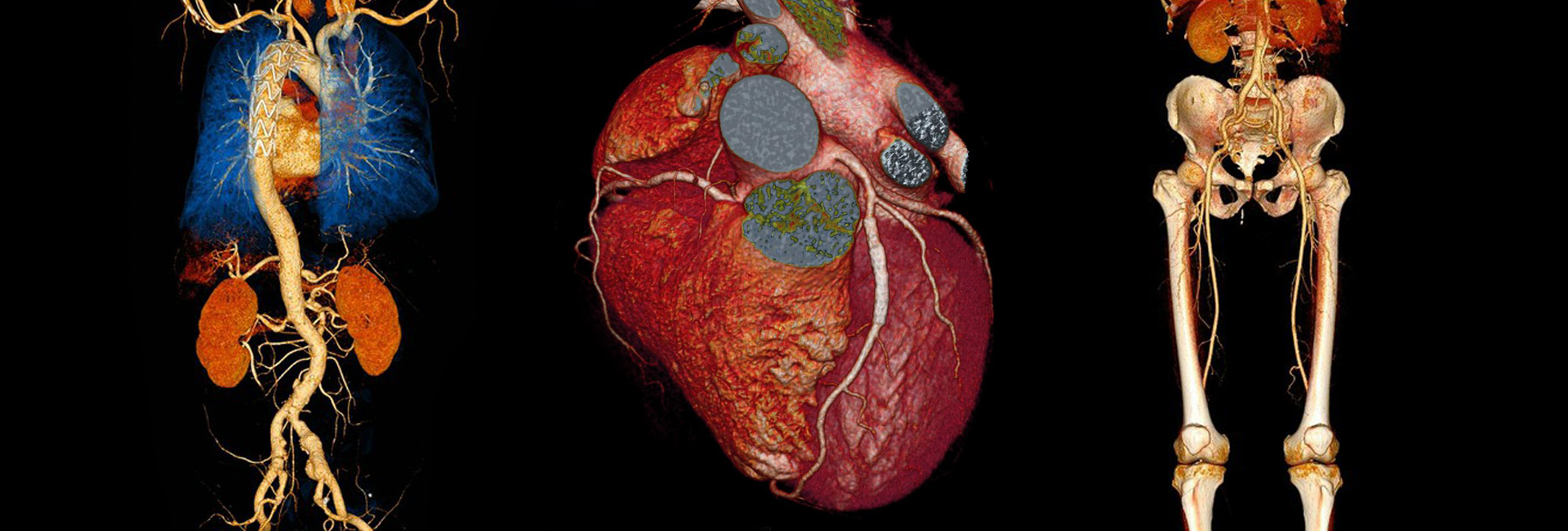
Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or related conditions, such as aneurysms or blockages.
CT angiography is used to examine blood vessels and the organs supplied by them in various body parts, including:
- Brain
- Neck
- Heart
- Chest
- Abdomen (such as the kidneys and liver)
- Pelvis
- Legs and feet
- Arms and hands
Physicians use this test to diagnose and evaluate many diseases of blood vessels and related conditions such as:
- Injury
- Aneurysms
- Blockages (including those from blood clots or plaques).
- Disorganized blood vessels and blood supply to tumors.
- Congenital (birth related) abnormalities of the heart, blood vessels or various parts of the body which might be supplied by abnormal blood vessels.
Also, physicians use this exam to check blood vessels following surgery, such as:
- Identify abnormalities, such as aneurysms, in the aorta, both in the chest and abdomen, or in other arteries.
- Detect atherosclerotic (plaque) disease in the carotid artery of the neck, which may limit blood flow to the brain and cause a stroke.
- Identify a small aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation (abnormal communications between blood vessels) inside the brain or other parts of the body.
- Detect atherosclerotic disease that has narrowed the arteries to the legs and help prepare for endovascular intervention or surgery.
- Detect disease in the arteries to the kidneys or visualize blood flow to help prepare for a kidney transplant or stent placement.
- Guide interventional radiologists and surgeons making repairs to diseased blood vessels, such as implanting stents or evaluating a stent after implantation.
- Detect injury to one or more arteries in the neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis or extremities in patients after trauma.
- Evaluate arteries feeding a tumor prior to surgery or other procedures such as chemoembolization or selective internal radiation therapy.
- Identify dissection or splitting in the aorta in the chest or abdomen or its major branches.
- Show the extent and severity of the effects of coronary artery disease and plan for a surgical operation, such as a coronary bypass and stenting.
- Examine pulmonary arteries in the lungs to detect pulmonary embolism (blood clots, such as those traveling from leg veins) or pulmonary arteriovenous malformations.
- Look at congenital abnormalities in blood vessels, especially arteries in children (e.g., malformations in the heart or other blood vessels due to congenital heart disease).
- Evaluate obstructions of vessels.
At our centre, we routinely performs triple phasic study on our multislice scanner.